Maternal Infant Health Program: Nurturing the Future
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Maternal Infant Health Program
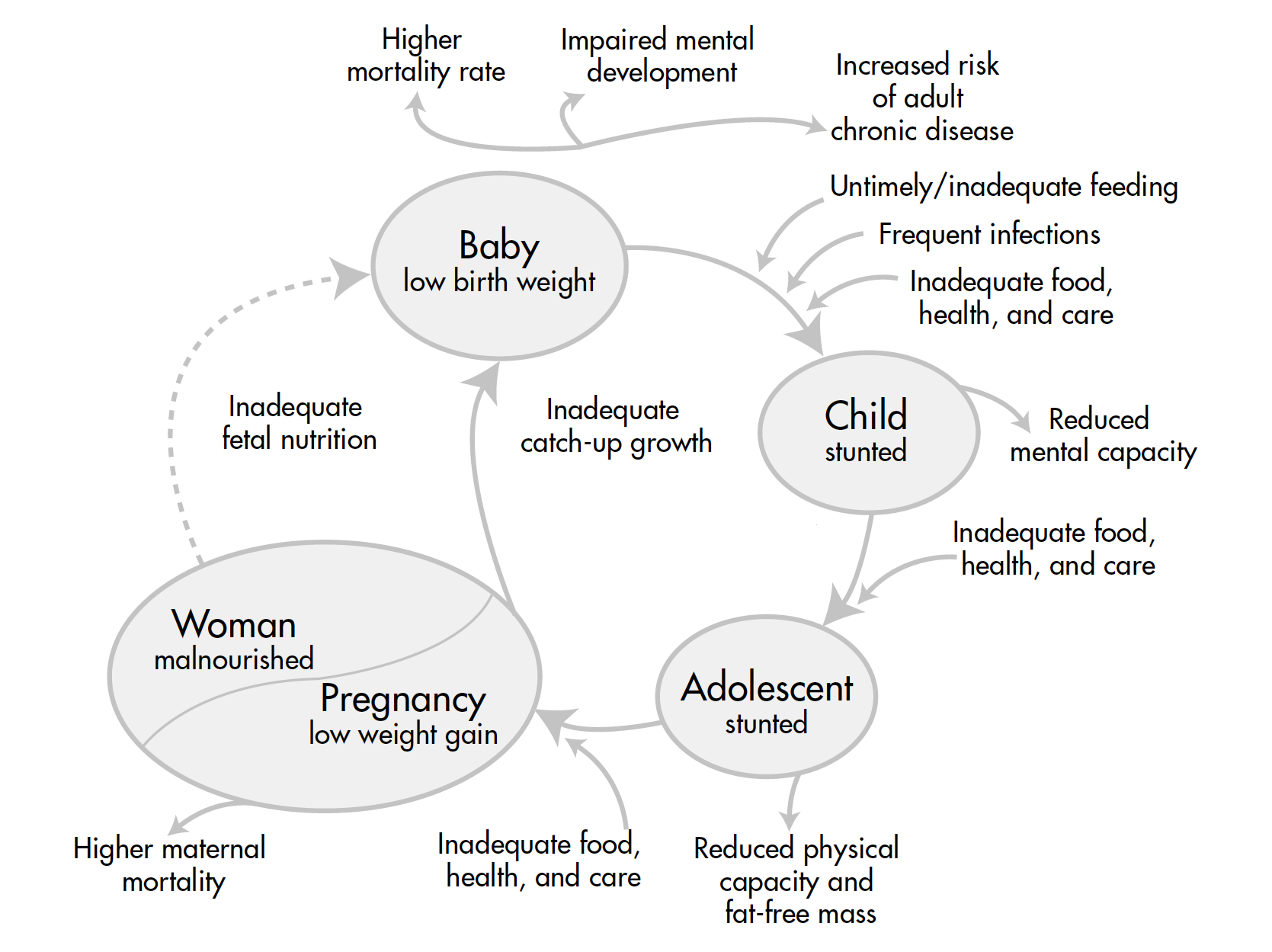
Maternal Infant Health Programs are comprehensive initiatives designed to safeguard the health of pregnant women and their infants. These programs encompass a range of interventions, from prenatal care to postpartum support.
B. Importance of Maternal and Infant Health
The well-being of mothers and infants is not only a fundamental human right but also a cornerstone for building healthy societies. Investing in maternal and infant health ensures a brighter and healthier future for communities worldwide.
II. The Need for Maternal Infant Health Programs
A. Global Maternal Mortality Rates
Despite advancements in healthcare, maternal mortality rates remain a concern globally. Maternal Infant Health Programs aim to reduce these rates through targeted interventions and accessible healthcare services.
B. Infant Mortality Statistics
Infant mortality, though declining, still poses a significant challenge. Maternal Infant Health Programs address this by focusing on early detection of potential issues, promoting proper nutrition, and ensuring timely vaccinations.
C. Disparities in Maternal and Infant Health
Socioeconomic and cultural factors contribute to disparities in healthcare access. Maternal Infant Health Programs work towards eliminating these disparities, ensuring that every mother and infant receives adequate care.
III. Goals and Objectives of Maternal Infant Health Programs
A. Enhancing Prenatal Care
Early and regular prenatal care is crucial for a healthy pregnancy. Maternal Infant Health Programs emphasize the importance of early check-ups, proper nutrition, and educational resources for expectant mothers.
B. Promoting Safe Delivery Practices
Ensuring a safe delivery is a primary objective. These programs advocate for skilled birth attendance, access to emergency obstetric care, and education on delivery preparedness.
C. Ensuring Postpartum Support
The postpartum period is equally important. Maternal Infant Health Programs provide support for mothers during this phase, addressing physical and emotional well-being, and offering guidance on infant care.
IV. Components of a Successful Maternal Infant Health Program
A. Accessible Healthcare Services
Proximity to healthcare facilities is vital. Successful programs ensure that healthcare services are easily accessible, especially in remote or underserved areas.
B. Education and Awareness Initiatives
Educating communities on maternal and infant health is key. Programs include awareness campaigns, workshops, and educational materials to empower individuals with knowledge.
C. Community Involvement
Engaging communities fosters a sense of ownership. Maternal Infant Health Programs actively involve local communities, seeking their input, and tailoring interventions to meet specific needs.
V. Success Stories
A. Highlighting Positive Outcomes
Real success stories underscore the impact of Maternal Infant Health Programs. Improved maternal and infant health outcomes showcase the effectiveness of these initiatives in creating lasting positive change.
B. Impact on Maternal and Infant Well-being
From reduced mortality rates to improved overall health, the impact of these programs extends beyond statistics. Maternal Infant Health Programs contribute to healthier communities and empowered mothers.
VI. Challenges in Implementing Maternal Infant Health Programs
A. Socioeconomic Factors
Financial constraints can hinder access to healthcare. Addressing socioeconomic factors is crucial for the success of Maternal Infant Health Programs.
B. Cultural Barriers
Cultural beliefs and practices may influence healthcare decisions. Programs incorporate culturally sensitive approaches to bridge gaps and ensure acceptance within diverse communities.
C. Healthcare Infrastructure
Inadequate healthcare infrastructure poses a challenge. Maternal Infant Health Programs advocate for improved infrastructure, ensuring that quality healthcare is accessible to all.
VII. Innovations in Maternal Infant Health Programs
A. Technology Integration
The integration of technology enhances healthcare delivery. Maternal Infant Health Programs leverage technology for remote consultations, monitoring, and educational purposes.
B. Telemedicine for Prenatal Consultations
Telemedicine has emerged as a valuable tool for prenatal care. Programs incorporate telemedicine to reach expectant mothers in remote areas, providing them with expert guidance.
C. Community-Based Interventions
Community-based interventions foster a sense of community responsibility. Maternal Infant Health Programs increasingly focus on grassroots initiatives, empowering communities to take charge of their health.
VIII. Future Prospects and Trends
A. Emerging Technologies in Maternal Health
Advancements in technology continue to shape healthcare. Maternal Infant Health Programs anticipate and embrace emerging technologies to enhance the quality and accessibility of care.
B. Advocacy for Policy Changes
Effective policies are integral to sustained progress. These programs advocate for policy changes at local and global levels, aiming to create an environment conducive to maternal and infant well-being.
C. Global Collaborations for Improved Health Outcomes
The interconnected nature of health requires global collaboration. Maternal Infant Health Programs foster partnerships between nations, sharing best practices and resources for improved health outcomes.
IX. Conclusion
A. Recap of the Importance of Maternal Infant Health Programs
Maternal Infant Health Programs play a vital role in ensuring the health and well-being of mothers and infants globally. By addressing challenges, leveraging innovations, and fostering community involvement, these programs contribute to creating a healthier future for all.
B. Call to Action for Continued Support
The journey towards better maternal and infant health is ongoing. Continued support, both at the individual and societal levels, is crucial for the success and expansion of Maternal Infant Health Programs.
X. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A. What is the primary goal of Maternal Infant Health Programs?
Maternal Infant Health Programs aim to safeguard the health of pregnant women and their infants by providing comprehensive care and support throughout the pregnancy and postpartum periods.
B. How do these programs address disparities in healthcare?
Maternal Infant Health Programs address disparities by focusing on accessible healthcare services, community involvement, and education, ensuring that all mothers and infants receive equal and quality care.
C. Are Maternal Infant Health Programs only for low-income populations?
No, Maternal Infant Health Programs are designed to benefit all pregnant women and infants, regardless of their socioeconomic status. These programs aim to provide inclusive and accessible healthcare for everyone.
D. What role does community involvement play in the success of these programs?
Community involvement is crucial for the success of Maternal Infant Health Programs. It fosters a sense of ownership, tailoring interventions to meet specific community needs, and ensuring the sustainability of health initiatives.
E. How can individuals contribute to supporting maternal and infant health?
Individuals can contribute by raising awareness, supporting local initiatives, and advocating for policies that prioritize maternal and infant health. Every small effort adds up to creating a healthier future for mothers and infants.
